Cryptography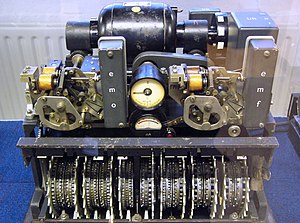 The German Lorenz cipher machine, used in World War II for encryption of very high-level general staff messages
The German Lorenz cipher machine, used in World War II for encryption of very high-level general staff messages
Cryptography (or cryptology; from Greek κρυπτός, kryptos, "hidden, secret"; and γράφω, gráphō, "I write", or -λογία, -logia, respectively)[1] is the practice and study of hiding information. In modern times, cryptography is considered a branch of both mathematics and computer science, and is affiliated closely with information theory, computer security, and engineering. Cryptography is used in applications present in technologically advanced societies; examples include the security of ATM cards, computer passwords, and electronic commerce, which all depend on cryptography.
Terminology
Until modern times, cryptography referred almost exclusively to encryption, the process of converting ordinary information (plaintext) into unintelligible gibberish (i.e., ciphertext). Decryption is the reverse, moving from unintelligible ciphertext to plaintext. A cipher (or cypher) is a pair of algorithms which creates the encryption and the reversing decryption. The detailed operation of a cipher is controlled both by the algorithm and, in each instance, by a key. This is a secret parameter (ideally, known only to the communicants) for a specific message exchange context. Keys are important, as ciphers without variable keys are trivially breakable and therefore less than useful for most purposes. Historically, ciphers were often used directly for encryption or decryption, without additional procedures such as authentication or integrity checks.
In colloquial use, the term "code" is often used to mean any method of encryption or concealment of meaning. However, in cryptography, code has a more specific meaning; it means the replacement of a unit of plaintext (i.e., a meaningful word or phrase) with a code word (for example, apple pie replaces attack at dawn). Codes are no longer used in serious cryptography—except incidentally for such things as unit designations (e.g., Bronco Flight or Operation Overlord) —- since properly chosen ciphers are both more practical and more secure than even the best codes, and better adapted to computers as well.
Some use the terms cryptography and cryptology interchangeably in English, while others use cryptography to refer specifically to the use and practice of cryptographic techniques, and cryptology to refer to the combined study of cryptography and cryptanalysis.
The study of characteristics of languages which have some application in cryptology, i.e. frequency data, letter combinations, universal patterns, etc. is called Cryptolinguistics.
This Beauty Care Must Be Done in the Morning
7 years ago


0 comments:
Post a Comment